Oil-immersed transformers are a cornerstone of modern electrical power systems, serving as crucial devices for voltage regulation, power distribution, and energy efficiency. At the heart of these transformers lies the transformer core, a carefully engineered component that significantly influences the overall electrical performance. In oil-immersed transformers, the design of the core directly impacts parameters such as efficiency, loss reduction, voltage regulation, noise levels, and thermal management. Understanding the connection between core design and electrical performance is essential for both engineers and utility operators seeking optimal transformer operation.
The transformer core serves as a magnetic circuit that guides the magnetic flux generated by alternating current (AC) in the primary winding to the secondary winding. In oil-immersed transformers, the core is submerged in transformer oil, which serves both as a coolant and insulating medium. The design of the core—its geometry, material, and construction—affects the magnetic properties and, consequently, the efficiency and performance of the transformer.
Key functions of the transformer core include:
Material selection is a critical aspect of transformer core design. High-performance cores use silicon steel laminations or amorphous metal alloys, which affect efficiency, losses, and operational stability.
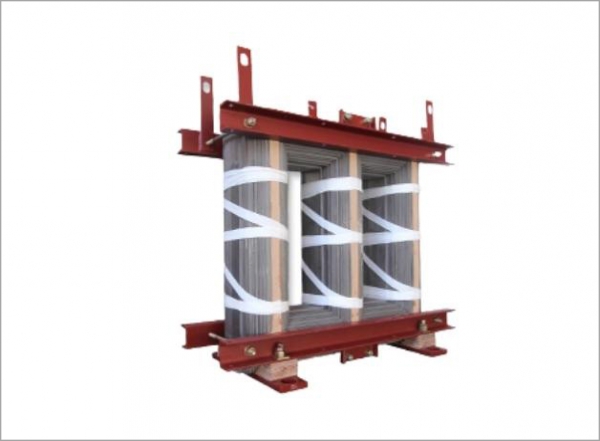

The way the core is constructed has a profound effect on magnetic properties, losses, and electrical performance.
Core-Type Transformers
Shell-Type Transformers
The physical dimensions and shape of the core influence key performance characteristics.
In oil-immersed transformers, the core interacts with the cooling system. The core’s surface area, orientation, and placement within the tank affect oil circulation and heat dissipation.
The design of the oil-immersed transformer core affects several critical electrical performance metrics:
Modern oil-immersed transformers incorporate advanced core designs to further enhance performance:
These innovations improve energy efficiency, reduce operational costs, and extend transformer lifespan.
The design of an oil-immersed transformer core is a critical factor that directly influences electrical performance, efficiency, thermal management, voltage regulation, and reliability. Material selection, lamination thickness, core geometry, joint design, and interaction with the cooling system collectively determine the transformer’s operational characteristics.
High-quality cores made from grain-oriented silicon steel or amorphous alloys, combined with optimized construction techniques such as step-lap joints and precise lamination stacking, minimize losses, improve efficiency, and enhance durability. Properly designed cores also reduce noise, prevent localized heating, and maintain stable voltage output, which is essential for both industrial and utility-scale applications.
As energy efficiency and reliability become increasingly important in modern power systems, the design of oil-immersed transformer cores will continue to evolve, incorporating new materials, innovative geometries, and precision manufacturing techniques to meet the demands of the future. Understanding the critical relationship between core design and electrical performance is essential for engineers, manufacturers, and operators seeking optimal transformer performance and longevity.
 +86-523 8891 6699
+86-523 8891 6699  +86-523 8891 8266
+86-523 8891 8266  info@tl-core.com
info@tl-core.com  No.1, Third Industrial Park, Liangxu Street, Taizhou City, Jiangsu, China
No.1, Third Industrial Park, Liangxu Street, Taizhou City, Jiangsu, China 

 English
English Español
Español Türk
Türk 中文简体
中文简体