Power distribution transformers play a critical role in ensuring that electrical energy is efficiently transferred across long distances and used by consumers. The core of a power distribution transformer is one of the most important components influencing its efficiency. In this article, we will explore the significance of the transformer core in relation to energy efficiency, how it impacts the overall performance of transformers, and how advancements in core materials and design have contributed to reducing energy losses in electrical systems.
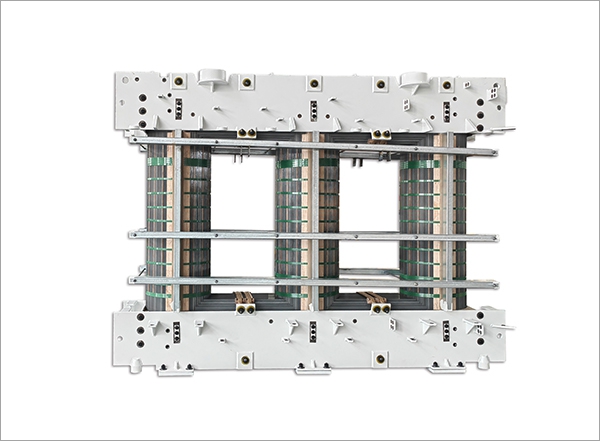
The transformer core is a vital part of the transformer’s operation. It is the component that channels the magnetic flux generated by the electrical current. The transformer core’s design directly impacts the efficiency of the energy transfer process. When electrical current flows through the primary windings of the transformer, it generates a magnetic field, which induces current in the secondary windings through the core. This induced current is then transferred to the load, making the transformer’s core essential for efficient energy conversion.
The materials used in the transformer core play a significant role in its energy efficiency. Traditionally, transformer cores were made from laminated sheets of electrical steel, which reduced the losses due to eddy currents. However, modern transformer cores often use advanced materials such as amorphous steel, which has a lower core loss due to its non-crystalline structure.
Core losses are one of the key factors that influence the energy efficiency of power transformers. These losses consist of two components: hysteresis loss and eddy current loss. Hysteresis loss occurs due to the constant magnetization and demagnetization of the transformer core during operation, while eddy current loss is caused by circulating currents induced within the core material.
By using high-quality, low-loss materials and improving the design of the core, these losses can be minimized. Innovations in core design, such as reducing the thickness of the laminated sheets and utilizing more efficient materials like amorphous steel, can help reduce energy waste and improve the transformer’s overall efficiency.
The physical design of the transformer core plays a significant role in its efficiency. Modern transformers are designed with cores that feature tight laminations to reduce eddy current losses. The core’s shape and size are also optimized for performance. In some cases, manufacturers may use toroidal cores or other advanced geometries to enhance energy transfer and minimize energy losses.
Additionally, the way the core is assembled impacts its efficiency. For example, the orientation of the core laminations, the alignment of the magnetic field, and the design of the windings all contribute to the transformer’s efficiency. Careful engineering ensures that the core efficiently channels the magnetic flux with minimal resistance, leading to reduced losses and improved energy efficiency.
Energy efficiency in power transformers not only impacts the immediate operation but also affects the long-term costs of the transformer. A well-designed core, using advanced materials and optimized construction, leads to lower operational costs due to reduced energy losses. Over the course of a transformer’s life, these savings can be significant, making it a wise investment for utilities and industrial applications.
Furthermore, transformer cores that are more energy-efficient tend to produce less heat, leading to a longer lifespan and reduced maintenance costs. The reduced need for cooling also lowers operating costs, making the investment in a high-quality transformer core a cost-effective choice for many industries.
In recent years, the development of new transformer core technologies has contributed significantly to improving the energy efficiency of power transformers. For example, the introduction of amorphous steel and nanocrystalline materials has greatly reduced core losses. Additionally, advances in core manufacturing processes, such as precision cutting and welding, have led to better core integrity, further enhancing performance.
The core of a power distribution transformer is integral to its overall energy efficiency. By choosing high-quality materials, optimizing the design, and implementing innovative technologies, transformer manufacturers can significantly reduce core losses and improve performance. As the demand for energy-efficient solutions grows, the continued advancement of transformer core technology will play a critical role in achieving sustainable energy systems.
Ultimately, understanding the role of the transformer core in energy efficiency can help utilities and industries make informed decisions when selecting and maintaining their power transformers. This can lead to long-term cost savings, improved system reliability, and a reduction in overall energy consumption.
 +86-523 8891 6699
+86-523 8891 6699  +86-523 8891 8266
+86-523 8891 8266  info@tl-core.com
info@tl-core.com  No.1, Third Industrial Park, Liangxu Street, Taizhou City, Jiangsu, China
No.1, Third Industrial Park, Liangxu Street, Taizhou City, Jiangsu, China 

 English
English Español
Español Türk
Türk 中文简体
中文简体