Oil-immersed transformer cores are a critical component in power distribution and transmission systems. These cores are submerged in insulating oil that serves multiple purposes: cooling, electrical insulation, and protection against oxidation. Proper maintenance and timely troubleshooting are essential to ensure their reliable operation, prevent failures, and extend service life. This article provides a comprehensive guide on effective maintenance strategies, common troubleshooting techniques, and best practices for operational efficiency.
The transformer core is typically made from laminated silicon steel sheets to reduce eddy current losses. Laminations are tightly stacked and insulated to enhance magnetic efficiency. Oil immersion helps dissipate heat generated from core losses and winding resistance while providing electrical insulation between the core and windings. Understanding the core’s structure is crucial for diagnosing potential problems and planning effective maintenance schedules.
Routine maintenance of oil-immersed transformer cores focuses on both the core and the insulating oil. A systematic approach includes periodic inspection, cleaning, and monitoring of operational parameters. Regular maintenance not only prevents failures but also improves transformer efficiency and longevity.
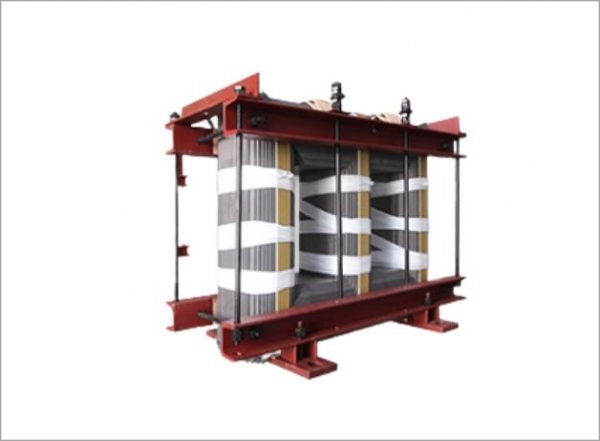

Regular visual inspections help identify obvious signs of wear or damage. Check for oil leaks, corrosion on the tank or fittings, and loose connections. Inspect bushings for cracks and confirm that the radiator fins or cooling channels are free of obstructions. Visual monitoring is a simple yet effective first step in early fault detection.
Insulating oil serves as both a coolant and an electrical insulator. Periodic testing is essential to monitor its quality. Key tests include:
Dust, dirt, and oxidation can compromise heat dissipation and insulation. Clean the core tank and radiator surfaces regularly. Ensure that cooling fans, pumps, and oil circulation systems are operational. Efficient cooling prevents overheating, a common cause of transformer core failures.
Even with proper maintenance, transformer cores may develop operational issues. Early identification and resolution are critical to avoid catastrophic failures. Common problems include overheating, insulation degradation, partial discharges, and abnormal vibrations.
Overheating can be caused by high load, insufficient cooling, or deteriorated oil. Monitor transformer temperature using sensors or infrared thermography. Reduce load or improve oil circulation as immediate measures. Inspect the core for signs of localized heating, which may indicate shorted laminations or winding issues.
Insulation breakdown is a major cause of transformer malfunction. Moisture ingress, aging oil, or excessive electrical stress can degrade insulation. Conduct insulation resistance testing and monitor dielectric strength. Replace or recondition oil and repair damaged insulation to prevent further deterioration.
Partial discharges inside the transformer core or windings may generate audible noise, ozone, or gas by-products. Use ultrasonic detection or DGA to identify discharge sites. Corrective actions may include tightening laminations, improving oil insulation, or addressing design flaws that concentrate electric fields.
Advanced monitoring techniques are vital for predictive maintenance and fault prevention. Regular diagnostic testing allows operators to plan maintenance proactively rather than reacting to failures.
DGA involves analyzing gases dissolved in transformer oil. Different gases indicate specific faults:
Infrared cameras detect hot spots on the transformer tank and radiator. Identifying temperature anomalies helps locate areas of excessive core losses, poor oil circulation, or winding faults. Early detection prevents catastrophic failure and reduces downtime.
Abnormal vibrations may indicate loose laminations or core shifting. Vibration sensors can detect subtle mechanical problems before they develop into larger failures. Regular monitoring of vibration levels is recommended for oil-immersed transformers under heavy load or in high-vibration environments.
Maintaining oil-immersed transformer cores effectively requires a structured approach. The following practices are widely recommended:
Oil-immersed transformer cores play a pivotal role in electrical systems, and proper maintenance is essential for safe and reliable operation. By implementing regular inspections, oil testing, thermal imaging, and vibration monitoring, operators can identify and address potential issues early. Adhering to best practices enhances transformer efficiency, prevents downtime, and extends service life. Effective troubleshooting combined with proactive maintenance ensures that oil-immersed transformers continue to perform optimally in demanding applications.
 +86-523 8891 6699
+86-523 8891 6699  +86-523 8891 8266
+86-523 8891 8266  info@tl-core.com
info@tl-core.com  No.1, Third Industrial Park, Liangxu Street, Taizhou City, Jiangsu, China
No.1, Third Industrial Park, Liangxu Street, Taizhou City, Jiangsu, China 

 English
English Español
Español Türk
Türk 中文简体
中文简体