Transformer cut laminations are critical components in electrical transformers, designed to reduce energy losses and improve overall performance. These thin sheets of electrical steel are precisely cut and stacked to form the magnetic core of a transformer. Their primary purpose is to minimize eddy current losses, which can lead to overheating and inefficiency if not properly managed.
The core of a transformer is responsible for directing magnetic flux efficiently between the primary and secondary windings. By using cut laminations rather than a solid core, transformers can significantly reduce eddy currents. Each lamination is insulated from the others, restricting the flow of circulating currents and thus reducing energy waste and heat generation.
The material used for transformer laminations is typically high-grade electrical steel with low hysteresis loss. This ensures that the magnetic flux can pass with minimal resistance, enhancing efficiency. The combination of material quality and precise cutting techniques determines the effectiveness of the laminations.
Each lamination is coated with an insulating layer, such as varnish or oxide, to prevent direct electrical contact. This insulation is essential to limit eddy currents, which are induced within the core material by alternating magnetic fields. Proper insulation improves the lifespan of the transformer and ensures stable operation under varying load conditions.
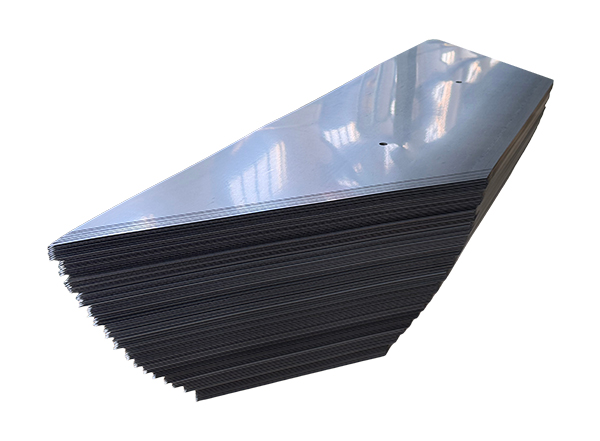

Transformer cut laminations offer multiple advantages, which make them indispensable in modern electrical equipment:
Transformer cut laminations are used in various types of transformers across industries, each requiring high efficiency and reliability:
The performance of transformer cut laminations depends on several critical factors:
Thinner laminations reduce eddy current paths, enhancing efficiency. Common thicknesses range from 0.2 mm to 0.35 mm for power transformers, balancing cost and performance.
The geometric design of the core, including the shape and stacking orientation of laminations, affects magnetic flux distribution and leakage. Optimized designs improve transformer performance and reduce stray losses.
High-quality electrical steel with low carbon content ensures reduced hysteresis loss. Grain-oriented steel is often used to align magnetic domains for maximum efficiency.
The manufacturing of transformer cut laminations involves precise cutting, stacking, and insulation:
Compared to solid core transformers, laminated cores provide:
Transformer cut laminations are essential components that enhance the efficiency, safety, and longevity of transformers. By minimizing eddy current and hysteresis losses, optimizing thermal management, and providing structural stability, these laminations ensure that electrical equipment operates reliably and cost-effectively. Industries ranging from power distribution to renewable energy benefit from the advanced design and material quality of cut laminations, making them a vital element in modern electrical systems.
 +86-523 8891 6699
+86-523 8891 6699  +86-523 8891 8266
+86-523 8891 8266  info@tl-core.com
info@tl-core.com  No.1, Third Industrial Park, Liangxu Street, Taizhou City, Jiangsu, China
No.1, Third Industrial Park, Liangxu Street, Taizhou City, Jiangsu, China 

 English
English Español
Español Türk
Türk 中文简体
中文简体