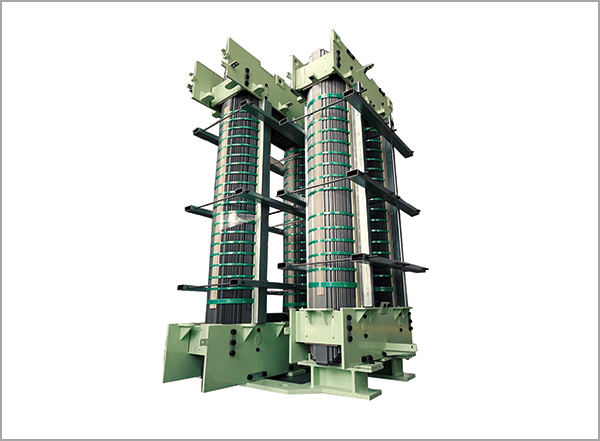
The core of a power distribution transformer is the central component responsible for magnetic flux conduction and energy transfer. Proper maintenance is critical to ensure optimal efficiency, reduce energy losses, prevent overheating, and extend the operational life of the transformer. Neglecting core maintenance can lead to insulation failure, increased noise, and reduced performance. This article delves into the key maintenance practices required for power distribution transformer cores.
Transformer cores are typically made from silicon steel laminations, amorphous steel, or laminated grain-oriented steel. Each type has unique properties affecting maintenance:
Visual inspections form the first step in transformer core maintenance. Technicians should look for signs of physical damage, such as bent laminations, loose stacking, or corrosion. Early detection of mechanical issues helps prevent severe faults and reduces downtime. Regular inspections should include checking for insulation deterioration, dust accumulation, and signs of overheating.
Monitoring core losses and operating temperature is essential to prevent energy inefficiency and overheating. High core losses can indicate insulation degradation or shorted laminations. Temperature sensors and infrared thermography can detect hotspots within the core, allowing timely intervention. Maintaining optimal temperature prevents excessive thermal stress on the core and surrounding windings.
The laminations of a transformer core are insulated to minimize eddy current losses. Maintenance includes:
Transformer cores can produce vibration and humming due to magnetostriction and loose laminations. Excessive noise often indicates maintenance needs. Regularly inspecting core clamping, tightening bolts, and ensuring proper alignment of laminations reduces vibration. Additionally, vibration damping materials can be applied where necessary to minimize mechanical stress and acoustic noise.
Environmental factors such as humidity, dust, and corrosive gases can deteriorate transformer cores. Maintenance strategies include:
Periodic electrical tests help ensure the core operates within safe limits. Common diagnostics include:
A regular maintenance schedule is critical to extend the operational life of transformer cores. Best practices include:
Maintaining a power distribution transformer core requires a combination of visual inspection, electrical testing, environmental control, and preventive measures. Proper care ensures minimal core losses, reduced noise, and extended operational life. Adopting a structured maintenance schedule and best practices helps utilities and manufacturers maintain transformer efficiency, reliability, and safety.
 +86-523 8891 6699
+86-523 8891 6699  +86-523 8891 8266
+86-523 8891 8266  info@tl-core.com
info@tl-core.com  No.1, Third Industrial Park, Liangxu Street, Taizhou City, Jiangsu, China
No.1, Third Industrial Park, Liangxu Street, Taizhou City, Jiangsu, China 

 English
English Español
Español Türk
Türk 中文简体
中文简体